Key Takeaway
IaaS is a cloud computing service where users can use computing infrastructure through the internet, while a cloud provider is responsible for hosting and maintaining it.
When developing an application, you know that each one has specific infrastructure needs like speed, reliability, and capacity. This means you will need to invest in and configure various components such as powerful hard drives, reliable network cables, servers, and routers that can handle your application's demands.
It sounds costly and complicated, and rightly so.
Alternatively, you can consider a more cost-effective and convenient option like using an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) that can provide you with the entire infrastructure over the cloud, a service so widely used by businesses that its market is predicted to reach around 195.45 billion U.S. dollars in 2024.
In this article, we cover the definition, types, examples, and pros and cons of IaaS.
What is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)?
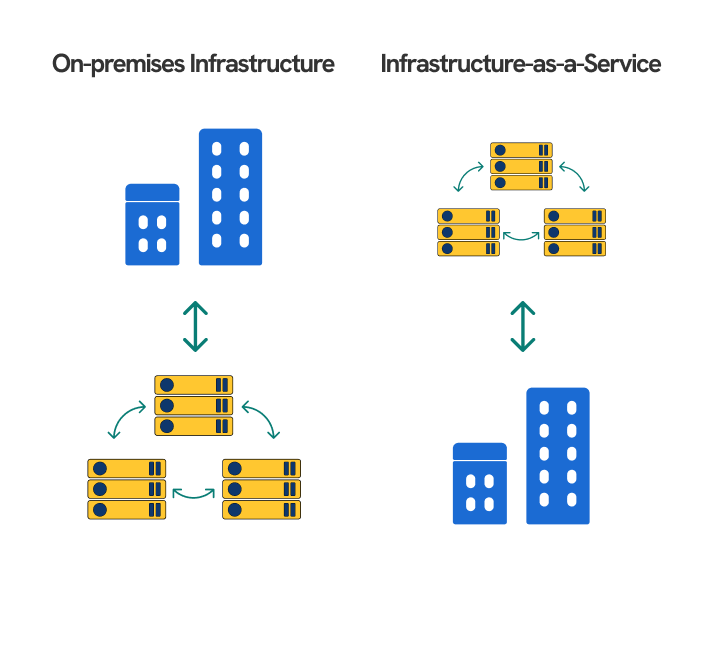
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing service where a provider hosts and maintains computing infrastructure in the cloud and lends access to users through the internet.
To give a clearer picture, computing infrastructure consists of the machines that run programs and store information and the equipment and wires that connect them. If you use IaaS, you can access these resources over the internet instead of having and maintaining physical machines yourself.
IaaS is a fundamental part of cloud computing services that includes Platform as a service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS)
💡 Tip: Read the difference between PaaS, SaaS, and IaaS in our informative article.
How Does IaaS Work?
In the IaaS model, the service providers are responsible for hosting, managing, and maintaining the physical infrastructure and resources on the cloud. They provide these resources through virtual machines that are accessible via the Internet. Meanwhile, users can focus on their applications and IT systems, access and configure the resources they need on demand and pay for what they use.
Let’s break down the details.
1. The Infrastructure Layer
IaaS has an infrastructure layer as its foundation.
This consists of the physical computing power hardware (such as CPU, PSU, RAM, hard disks), networking hardware (such as routers, switches, firewalls, load balancers, VPNs), storage capacity (such as block storage, file storage, object storage) and security for the cloud services.
The cloud provider owns and manages the infrastructure layer, which ensures its availability and reliability.
2. Virtualization Technology
In short, virtualization technology creates simulated computer systems that operate separately from the original physical devices. The IaaS model uses this technology to create multiple “virtual machines (VMs)” from its infrastructure layer, each with its operating system and applications to lend to users.
The providers can also use virtualization to abstract and pool the infrastructure layer resources (such as CPU and network bandwidth) and dynamically allocate them to the VMs as needed.
In this way, cloud providers can optimize physical resources and offer more flexibility and scalability to users.
3. Scaling
When demand fluctuates, there is a need for scaling.
In the IaaS model, scaling refers to increasing or decreasing the number of VMs or the size of each VM.
This can be done manually by the user through a web portal or an API, or automatically done based on traffic load, CPU utilization or other predefined triggers.
4. Maintenance and Resource Allocation
Maintenance involves updating, patching, repairing, or replacing physical or virtual backend components. Resource allocation refers to the distribution of resources among the many VMs. Both are key tasks in optimizing the cloud infrastructure's performance, reliability, and efficiency.
Cloud providers typically handle these tasks behind the scenes without affecting the user experience.
Types of IaaS
The main types of IaaS include public IaaS, private IaaS, and hybrid IaaS. This is categorized by the type of cloud utilized.
Public IaaS
Public IaaS refers to Infrastructure as a Service where the underlying infrastructure resources are hosted on a public cloud, accessible to and utilized by multiple organizations. Users have limited control over the configuration and security of the infrastructure.
This IaaS option is cost-effective, with high availability, and ideal for workloads that vary in demand but do not require strict security.
Private IaaS
Private IaaS refers to an infrastructure that is hosted within a private cloud. Users have greater flexibility in managing the resources, which are shared exclusively within the organization.
This type of IaaS offers higher privacy and security, but also higher costs.
Hybrid IaaS
Hybrid IaaS combines public and private IaaS, sharing some resources while keeping others private. You can benefit from both cloud infrastructures for different purposes and workloads.
For example, you keep a workload that needs high availability on the public cloud while keeping sensitive ones on the private cloud.
Examples of IaaS Tools
Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2
Amazon Web Service (AWS) provides a wide range of cloud services, with Amazon EC2 as IaaS. EC2 offers secure and scalable computing capacity in the cloud and allows users to launch virtual machines (VMs) on Amazon’s infrastructure.
Amazon EC2 offers various instance types, storage options, processors, networking, operating systems, and purchase models. Its on-demand infrastructure and capacity have an SLA commitment of 99.99% availability. Users can also connect with an expert for support and guidance.
Expert Insight
AWS is a great cloud service provider, comprising a lot of services making it a complete solution for all the cloud computing requirements. It is easy to scale the infrastructure on AWS and adopt more services in the architecture. All of the services are highly available, secure and reliable.
OpenStack
OpenStack lets you manage different types of resources such as computing, storage, and networking through a dashboard or the OpenStack API.
Apart from standard IaaS service, it offers extra features such as orchestration, fault management, and compatibility with many common open-source technologies, allowing for smooth integration with diverse infrastructure.
IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud is a full-stack cloud platform with comprehensive products, such as developer tools, IoT, storage, networking, and security.
Its IaaS solution enables access to enterprise-grade & customizable hardware, on-premises data centers, over 20 TB free bandwidth integration, one of the highest network performances, and scaling in over 60 data centers.
Pros and Cons of IaaS
Now that we’ve covered what IaaS is and how it works, let's take a closer look at its pros and cons.
Advantages of IaaS
| Pros of IaaS | Description |
| Cost-Effective Approach | Using IaaS lets businesses be in control of their budget as they pay only for what they use. |
| Highly Scalable | Businesses need more resources to handle peak workloads. By using IaaS, companies can scale their infrastructure in minutes when they need it. |
| Easy to Deploy and Automate | With IaaS, you shift the infrastructure management to the provider. |
| Innovative and Pioneering Features | IaaS allows you to try and experiment with new product ideas, and innovations in a faster and more affordable way. (load balancing, disaster recovery etc) |
| Higher Uptime | Most widely-used IaaS providers guarantee 99.99% uptime. |
Cost-Effective Approach
The expenses of on-premises infrastructure go beyond the initial purchase. Not only do you need to invest in hardware and networking equipment, but you must also configure them, employ personnel to manage them, and secure space to house them.
With IaaS, there is no need to purchase, install, upgrade, or repair hardware. Costs related to power, space, and personnel are also minimized. Instead, you opt for a subscription or a pay-what-you-use model.
That said, the cost for the on-premise server can be about $2,500, while a cloud server may cost only $400.
💡 Caution: Despite this pro, 82% find cloud spending challenging. Unexpected costs can stem from bandwidth consumption, thus monitoring usage is essential.
Highly Scalable
Scaling is inevitable, whether due to seasonal fluctuations or unexpected demand.
However, scaling on-premises infrastructure is costly. Companies need to invest in additional equipment and servers for peak workloads, only to scale back down when the demand subsides. This process requires significant time and labour, with no guarantee of timely results. It leads to excessive spending on temporary resources. Not to mention wasted time and energy.
IaaS offers on-demand scaling, allowing businesses to increase or decrease data storage and computing resources as needed with a pay-for-use model.
What's more, scaling with IaaS takes only minutes to complete. This is possible because IaaS providers have robust storage, equipment and networking technology to cater to clients from the outset.
Easy to Deploy and Automate
Building, maintaining, and integrating IT infrastructure isn't easy. Simply put, the complexity of IT operations is shifted to your cloud provider if you’re using IaaS.
You can access resources through web-based interfaces or APIs that support the automation of various tasks such as provisioning, backup, and recovery.
This frees up time and energy, so IT specialists can focus on building new products and services.
Innovative and Pioneering Features
As providers consistently improve their offerings to stay competitive, customers can take advantage of these innovations without the need for significant investment or maintenance concerns.
Higher Uptime
Uptime refers to how long a service remains available, while downtime is when it gets shut down. Ideally, we want a service to always be available.
Prominent IaaS providers promise up to 99.99% uptime, meaning the service is only down for about 8.6 seconds per day. Achieving this level of uptime may be challenging for on-premise infrastructure.
Again, this is possible because IaaS providers have more resources and can run services on clustered systems.
Disadvantages of IaaS
| Cons of IaaS | Description |
| Finite Control Over the Underlying Infrastructure | Since the IaaS provider supplies the infrastructure, users have less control over it. |
| Inherent Security Risks | As a cloud-based service, cyberattacks can happen. |
| Internal Resources and Training | The company needs to spend time and resources on training employees on how to use IaaS. |
Finite Control Over the Underlying Infrastructure
IaaS users have limited control and visibility over the physical infrastructure that hosts their data and virtual machines. They rely on the cloud provider's service level agreements, security measures, compliance standards, and support services.
Inherent Security Risks
Security is a common challenge in cloud computing services.
While cloud service providers employ various security measures, such as regular OS updates and reinforced firewalls, data breaches can still occur. The cloud platform as a whole remains susceptible to hijackers, cyberattacks, leaks, and malware.
In an IaaS environment, users must adhere to best practices for security, but they will face difficulties addressing breach when it occurs. This is because users have limited control over cloud security.
However, whether cloud security is better or worse than on-premise infrastructure is a complicated question. The bottom line may be that both can be vulnerable to errors and breaches due to human factors.
To bridge this security gap, the most important step is to choose a reputable cloud provider, carefully review its service level agreement (SLA) and understand its security obligations.
Internal Resources and Training
Lack of resources and expertise is another common cloud computing challenge.
To effectively utilize IaaS, organizations need sufficient internal resources and skills. This involves training their staff on using the cloud provider's tools, monitoring and troubleshooting, integrating with other systems, and ensuring compliance.
The best way to tackle this challenge is to look for a provider with comprehensive customer support.
5 Things to Consider Before Choosing Iaas
Finding vendors for IaaS might not be as simple, so it’s time for serious questions, such as
1. How secure is the IaaS?
Since you are entrusting your data and applications to a third-party provider, you need to ensure that they have adequate security measures in place.
It is recommended to evaluate the following information of the provider:
- Encryption of data
- Potential configuration mistakes
- User permission management
- Data storage location
- Available redundancies in case of an outage
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs) that guarantee fast infrastructure fixes
Moreover, you should understand the scope of your own responsibilities for securing your data on the cloud.
Expert Insight
While choosing the IaaS providers, it is important to understand the shared responsibility model and understand who is responsible for what part of security. For example - In AWS, customers are responsible for infra patch management with regards to guest OS and applications, so it is vital to secure systems against ever-changing cybersecurity threats.
Our advice: Look for certifications. For example, SSAE 16 auditing standard, SOC 2 Type 2 attestation standard and ISO/IEC 27001 information security standard.
2. How Scaleable Is the IaaS?
IaaS's ability to scale is a major advantage, but not all IaaS are equal at scaling.
Take into account how fast can they scale and how automated is the scaling. It's best to choose IaaS which can quickly and automatically adjust resources based on preset rules, rather than needing manual intervention or approval.
Our advice: Compare scalability along with pricing and SLAs.
3. What Support Does the IaaS Include?
With IaaS, you depend on a cloud provider to run the infrastructure, so you will want their timely support in case of any issues that disturb your business flow.
Ideal providers should offer technical guidance and assistance for setting up and managing your infrastructure on the cloud. You also need a provider that has qualified experts available 24/7 through various communication channels like phone, email, and chat, to ensure the reliability of your operations.
Our advice: Ask about their response times. Additionally, read reviews of other customers regarding the provider’s support to get an accurate picture.
4. What Is the Cost of IaaS?
IaaS pricing looks very appealing compared to owning and maintaining your own infrastructure. Providers offer flexible plans, such as subscriptions or usage-based pricing.
However, it's crucial to grasp the overall cost involved.
Factor in the following:
- Your data usage
- Expenses for adapting existing applications
- Data transfer costs
- Potential surcharges during peak times that could exceed your budget
- Billing frequency
Our advice: Apart from the pricing structure, ask about the options for monitoring and deactivating unnecessary resources.
💡 Tip: Alternatively, learn how to upgrade your business without spending a dime with these Free SaaS Solutions.
5. Can the IaaS Be Migrated?
What if you decide to switch vendors or move from a cloud to an on-premise structure? This kind of migration can be challenging.
It’s important to make sure from the start that your provider allows for easy migration both in and out of their service.
Our advice: Negotiate the process and understand the agreement in your contract before signing to avoid vendor lock-in.
Final Thoughts
With IaaS, you can avoid the cost and complexity of buying and managing your physical servers and other data center infrastructure. This allows your team to focus on core business products and reduce the time and resources spent on IT infrastructure management.
FAQs
What is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud-based service that lets subscribers access and use virtual infrastructures hosted by a cloud provider.









