Key Takeaways
An invoice is a document issued by a seller to a buyer to request payment for the products or services provided. It includes transaction details, such as invoice number, service or product details, payment terms and methods, the total cost, and due date.
There are 13 types of invoices, and the most commonly used ones are the standard invoice, proforma invoice, commercial invoice, and retainer invoice. Understanding how to use different invoice types is essential for effective business operations.
For businesses, understanding how to use invoices correctly is crucial for efficient management operations.
No matter which industry you are in, you will have to encounter different types of invoices, from standard invoices to commercial invoices, recurring invoices, credit memos, and more. It is essential to know the differences in order to choose the right one to use.
This article explains what an invoice is, what the 13 types are, and how to use them. We also include useful tips for managing invoices so you can send invoices fast and always get payments on time.
What Is an Invoice?
An invoice is a document issued by a seller to a buyer to request payment for the products or services provided. It includes transaction details, such as invoice number, service or product details, payment terms and methods, the total cost, and due date.
Usually, businesses send invoices to collect payment from their customers after the purchased service or product is delivered. An invoice is a practical document in the accounting and auditing system, and many businesses across different industries use it. Apart from collecting payment, some invoices are essential for record-keeping and customs clearance purposes.
💡 Important: Technically, invoices and bills are different. However, in some contexts, some customers may refer to an invoice as a bill. It is essential to communicate between the seller and the buyer to avoid any disputes.
Example of an Invoice
Invoices may look different depending on their type, and each business might have its own invoice template. Still, they usually follow a similar structure and include the same key information about the purchase.
Let's take a look at an example of an invoice.
To ensure a successful payment from your clients and to avoid having to chase outstanding invoices, you should always include the following information clearly:
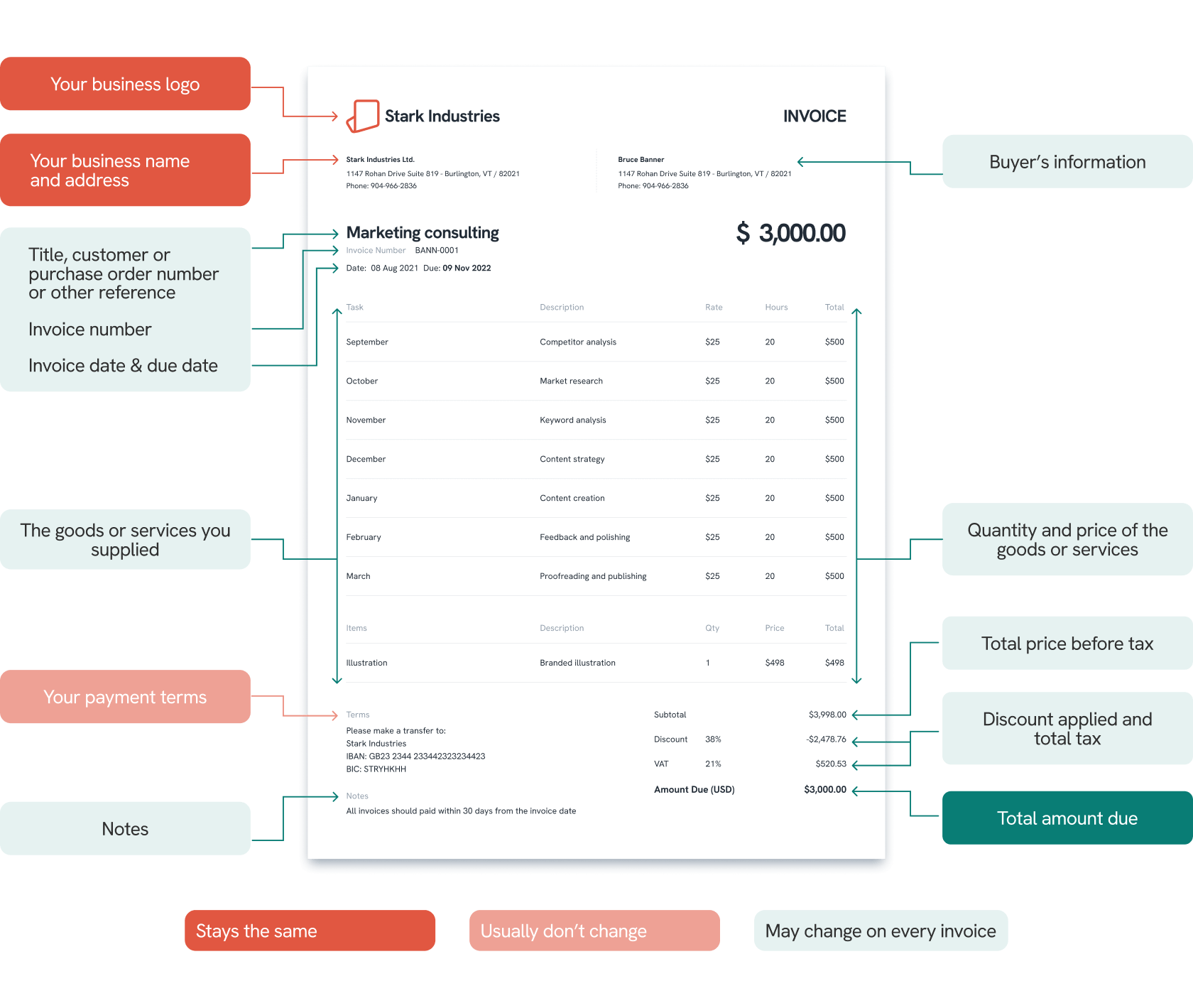
- Seller's information: This includes the company's logo, name, address, business contact information, and registration number.
- Buyer's information: This includes the customer's name, address, and contact details.
- Invoice number: This is a unique set of numbers that can identify and track each invoice. It can be composed entirely of numbers, letters, special characters, or a combination of everything, but it is vital to keep a consistent numbering system.
- Invoice date: This is when the invoice is issued, not the date of purchase. The invoice date is relevant to the payment due date, especially when the payment terms specify a payment period, for example, within 30 days.
- List of goods or services supplied: This includes the description of each item, quantity, price per unit, etc. Provide as much detail as possible to ensure that your customers know what they're paying for and can verify that everything is correct.
- Tax and discount information: Provide details of any applicable discounts, taxes, or fees, such as early payment discounts, VAT, or shipping fees. It is also essential to include the total price before tax on the invoice.
- The total amount due: The final amount after factoring in all discounts, taxes, and fees that the customer has to pay.
- Payment due date: This is the date by which your customer must pay you in full. Common payment due dates include net 30 (payment due within 30 days of the invoice date), net 15 (payment due within 15 days of the invoice date), or due upon receipt (immediate payment required).
- Payment terms: This includes details about payment methods, currencies, late fees, and other conditions related to the payment process.
💡 Tip: Although the format may vary, clarity is crucial when creating an invoice. Always ensure that you follow the invoicing best practices and that the details are clear for your customers, especially the total amount, payment terms, and due date.
All Invoice Types, What They Are, and When To Use Them
Depending on the purpose of issuing, the type of industry, the type of transaction, legal requirements, and specific business needs, there are several types of invoices that businesses could use.
In order to ensure seamless transactions and receive accurate payments on time, it's crucial to use the appropriate invoice type that suits your business's needs.
Here's a summary of the main types of invoices and when to use them:
| Types | What Is It | When To Use It |
| Standard Invoice | A general sales invoice | Issued after goods or services have been provided |
| Commercial Invoice | An invoice used for customs clearance to assess import duties and taxes | When making international trade |
| Pro Forma Invoice | An initial invoice sent before the delivery of products or services | When providing a preliminary invoice to confirm the order |
| Past-due Invoice | An invoice reissued to collect overdue payment, often with additional late fees | When an invoice is past a due date |
| Retainer Invoice | An invoice issued to secure future services | For a work-for-hire contract, typically legal services |
| Interim Invoice | An invoice issued for partial payments | When requesting payment for a portion of the total cost of the project |
| Timesheet Invoice | An hour-based service invoice | For hourly services |
| Recurring Invoice | An invoice that is issued on a recurring basis, usually monthly or annually, for ongoing goods or services | For ongoing services, subscriptions or installments |
| Credit Invoice | An invoice for overpayment, returned products, refunds, cancellations, or other issues in the customer's favor | When credit is due to the customer |
| Debit Invoice | An invoice issued to collect any additional charge | When there is an additional charge or minor changes to the original invoice |
| Mixed Invoice | A combination of a credit and debit invoice | When there are both credits and debits to be applied to the customer's account |
| Final Invoice | A final invoice that concludes a business agreement and requests payment | After a project or service is completed or as a final follow-up of other invoices |
| E-invoice | Any invoice that is sent and received electronically | When an invoice in an electronic form is preferred or required |
Now, let's take a closer look at each different type of invoice in detail.
Standard Invoice
A standard invoice is a regular sales invoice that provides the buyer with details of the purchase, including the total cost due and how to make the payment. This type of invoice often has a simple and flexible format that fits most industries.
For most businesses, a standard invoice is a sufficient document to request payments for the purchased goods or services from the customers. The invoice also serves as legal proof of the transaction after the payment is completed. In addition to this, the seller may also provide a receipt of payment to confirm the transaction as well.
When to Use a Standard Invoice
- When collecting payment from the customers.
- Normally, an invoice would be sent to request the payment after the service was provided or the goods were delivered.
Example: Starr Industries produced and delivered 60 precision machine parts to the buyer and now needs to collect payment. Starr Industries can issue a standard invoice to the customer, outlining the quantity, unit price, and total amount for the machine parts, as well as providing payment details and terms, such as wire transfer within 30 days.
Commercial Invoice
A commercial invoice is an invoice that is mainly used in international trade. It is an important document for businesses that export and import goods to collect payment from abroad and for customs authorities to determine applicable import duties and taxes. Normally, a commercial invoice requests the final price of the goods or services, including all related expenses, such as shipping fees.
This type of invoice contains details of the purchase that are crucial to the customs process. Hence, businesses must be extremely cautious when creating one, as mistakes can cause delivery delays.
It is mandatory to provide a commercial invoice when importing goods to some countries, and failure to do so may result in the goods being held at customs or returned to the sender.
When to Use a Commercial Invoice
- When shipping goods internationally and complying with international trade regulations.
Example: Starr Industries, a business based in Hong Kong, received an order from a client in Canada to produce 600 machine parts. In order to facilitate the customs process, Starr Industries includes a copy of a commercial invoice when shipping the products overseas to the client so the duties and taxes are calculated accordingly.
Pro Forma Invoice
A pro forma invoice, also spelled as a proforma invoice, is a preliminary invoice sent to the buyers before the delivery of goods or services. It includes details of the purchase, such as the products, estimated cost, logistic information, and more.
A pro forma invoice is a practical document to get an order confirmation from the buyers, as it allows the customer to review the purchase, estimate the cost, and negotiate terms. The seller and the buyer can use this invoice to communicate and ensure mutual agreement before finalizing the transaction.
Businesses in international trade can also issue a pro forma invoice to help estimate import duties and for customs purposes. However, it is different from a commercial invoice as a pro forma is not a legally binding document.
When to Use a Pro Forma Invoice
- When confirming a large order with a customer.
- When declaring the value of exporting or importing goods to customs.
- When bidding on a project, a proforma invoice can be sent as part of a proposal.
- A company that provides services to a foreign client may opt to send a pro forma invoice to the client before beginning any work.
Example: Starr Industries received an order of 60 precision machine parts. The company can send a pro forma invoice to the customer, stating the price per unit, the total cost, and any discounts. The customer can review if Starr Industries got the order correct, from the quantity ordered to the agreed price per unit, and then inform them to begin the manufacturing process without having to pay yet.
Past-due Invoice
A past-due or overdue invoice is an unpaid invoice that is past its payment period or specific due date. When the customer fails to pay on time, the supplier could reissue the invoice, send a reminder to notify the buyer of late fees or interest according to the payment terms, or take legal action.
When to Use a Past-due Invoice
- An invoice of any type is automatically past-due when it is unpaid past the payment due date.
Example: Starr Industries has stated in the invoice that they expect payment within 30 days, but it has been 40 days from the invoice issue date, and they haven’t received any payment from the customer. In this case, Starr Industries can send a reminder notice to the customer, requesting a full payment as soon as possible with a $100 late fee.
💡 Tip: For businesses that often have to deal with past-due invoices, it might be time to review your invoice template if the details are stated clearly. For customers, setting up a reminder is one way to improve your invoice payment management.
Retainer Invoice
A retainer invoice is an invoice for future service. Essentially, a retainer invoice requests a client to pay in advance for work that will be done in the near future or to secure a service to be used when needed. It can be thought of as a deposit or pre-payment to reserve services or to prevent cancellation. This invoice is often used for professional services like a consultant, advisor, lawyer, etc.
A retainer invoice is often sent along with a legally binding retainer agreement.
When to Use a Retainer Invoice
- When providing professional services.
- When a retainer agreement is in place.
Example: A client needing legal assistance contacted Starr Legal Services. As the client does not know the exact period when the service would be required or how long they would need the service, Starr Legal Services sends a retainer invoice following a retainer agreement to the client to secure payments for the company and to make sure that a lawyer is available for the client's case.
Interim Invoice
While working on a large project, interim invoices help divide payments into smaller parts. They are sent at pre-agreed milestones during the project's progress, requesting payment for each completed portion. Interim invoices ensure vendor cash flow and avoid burdening the buyer with a hefty sum.
When to Use an Interim Invoice
- When working on projects that take several months to complete, for example, construction projects, software development projects, and marketing campaigns.
Example: Starr Construction Services was contracted to work on a 12-month building project. To maintain an adequate supply budget, they agreed with the client to issue an interim invoice for payment upon completing every quarter of the total project.
Timesheet Invoice
A timesheet invoice is a hybrid of a timesheet and an invoice. It is used when the total cost of service is calculated based on the hours that the employee works to complete a project.
This invoice is commonly used by service-oriented businesses that charge customers for billable hours and is typically implemented throughout the project. A timesheet invoice usually records the start and end date of the project, the tasks, hourly charges, total hours, and total charges.
When to Use a Timesheet Invoice
- When providing professional service and charging by hours.
Example: Let's say a consultant works at the standard rate of $150/hour. If hired to work for 20 hours, a consultant can issue a timesheet invoice requesting payment of $3,000.
Recurring Invoice
A recurring invoice is an invoice issued to the same customer for the same amount of money and for the same service at a regular intervals. Sometimes, a pre-agreed-upon payment is automatically deducted from the customer's account.
If the customer fails to make a payment on time, the vendor might withhold the service or choose to cancel it for that payment term.
This invoice is a convenient choice for businesses that offer subscriptions, such as internet service providers, streaming services, cleaning services, or food suppliers.
When to Use a Recurring Invoice
- When the businesses deliver supplies or services regularly, like weekly cleaning or quarterly maintenance contracts.
- When the business uses a subscription model where the same bill is sent out each period.
- When the business requires payment in installments, such as car dealerships.
Example: Starr Cleaning Services provides a weekly cleaning package for apartments. They may send a recurring invoice to the clients every Friday to cover the service provided.
Credit Invoice
A credit invoice, also known as a credit memo or credit note, is a document used to notify a client that they are receiving reimbursement in the form of credits from the seller. This may follow invoice errors, customer overpayment, discounts, refunds, returned items, or order cancellation.
Regardless of the reasons the credit is offered, the seller should always generate a credit invoice to record the transaction.
This invoice always displays a negative total amount. For example, if a refund of $20 is issued, the credit invoice would be written as - $20
When to Use a Credit Invoice
- When there are issues in the customer's favor, such as damaged goods, order delays, missing order, etc.
- When there is an overpayment and credits need to be given back to the customer.
- When a customer receives a discount after they have paid the full amount.
Example: The client received the machine parts they ordered from Starr Industries, but the delivery arrived 3 days later than expected, which caused a minor disruption in the company’s operation. Starr Industries then offers a $200 credit to the client to redeem in the next purchase.
Debit Invoice
A debit invoice, also known as a debit memo or debit note, is used to add additional charges to the outstanding amount or to make a minor adjustment after the invoice is issued and received.
Usually, the seller would issue a debit invoice to the buyer when the total charge has been increased. However, it can be used when a time-based service takes longer than expected, but it is important to inform the customer first.
When to Use a Debit Invoice
- When the customer increases the quantity of their order
- When there is a miscalculation of additional charges such as tax or delivery fees.
Example: Starr Industries already sent an invoice to the client requesting $2400 as a payment for the 60 machine parts they supplied. However, the delivery fees need to be recalculated, resulting in an additional cost of $80. They can send a debit invoice to the client for the additional charge.
Mixed Invoice
A mixed invoice includes the details of both credit and debit invoices and provides the accumulated total amount. The outstanding amount could be owed to either the buyer or the seller.
When to Use a Mixed Invoice
- When errors favor the client and the buyer.
- When you are combining credit and debit invoices.
- When you need to decrease the amount the client owes but simultaneously increase it.
Example: Starr Industries issued a credit invoice worth $200 to the client and a debit invoice requesting an additional $80. In this case, Starr Industries can subtract the $80 fee from the $200 credit and send a mixed memo to inform the buyer of how they will repay the remaining $120.
Final Invoice
A final invoice is an invoice that concludes the total cost due for products or services rendered after deducting the amount charged by a retainer or interim invoice. It is usually sent to collect the remaining payment upon the completion of a project.
A final invoice includes details similar to a standard invoice, such as information about the product or service, invoice number, invoice date, and total amount. But if an amount was deducted prior to the end of the project, the business should address this in the invoice as well.
When to Use a Final Invoice
- When a project is complete.
- When issuing a final payment agreement after a proforma invoice.
Example: After completing a building project, Starr Construction Services issues an invoice to the client, requesting the remaining amount after deducting the amount paid according to the interim invoices.
E-invoice
Electronic Invoice is an umbrella term referring to any invoices sent electronically, regardless of their specific types. For instance, as an attachment in an invoice email.
When to Use an E-invoice
- When an electronic invoice is preferred.
- When a business wants the invoice to be conveniently shared among many stakeholders.
- When a business uses an automated invoicing system.
🔍 Discover: Not only do electronic invoices help speed up the invoicing process, but generating paperless digital invoices also reduces waste. Find out more about the pros and cons of e-invoice in our article.
8 Tips To Manage Invoices Effectively
Invoicing can be time-consuming without efficient invoice management. Here are 8 tips to manage your invoicing effectively and avoid disruptions such as disputes or payment delays.
1. Use Invoicing Software
Apart from saving time and reducing human errors, there are several reasons that you should consider using invoicing software to manage your invoices. Here are some of the significant benefits:
- Time efficiency - With its automatic process, Invoicing software can help save time from doing manual and repetitive tasks such as creating invoices, calculating totals, sending reminders, and applying taxes or discounts.
- Accuracy - Invoicing software can reduce the chances of errors in calculations or data entry.
- Easy payment tracking - You can save your invoices in one place and conveniently track payments, monitor overdue invoices, and look at an overview of your cash flow.
- Automated report - Invoicing software can generate monthly, quarterly, or annual reports, so you don't have to spend time gathering past invoices and analyzing them manually.
- Scalability - As the business expands, the number of invoices that need to be issued will also increase. Using automated software helps streamline the invoicing process when you have a larger client base.
Depending on your business's needs, there are several invoicing tool providers that you can choose from, such as PayPal Invoice, Invoice2go, Zoho Invoice, ZipBooks, and Statrys Invoicing Software.
🔍 Tip: See the 5 best free invoicing software in the market.
2. Send Out Invoices Promptly
Sending out invoices immediately after goods are delivered can enhance the chances of timely payment, which improves cash flows and minimizes the risk of disputes.
To speed up the process of issuing invoices, consider adopting these practices:
- Keep an accurate and up-to-date record - Maintaining up-to-date records is essential. When the record is outdated and unorganized, it becomes challenging to identify orders, making it challenging to track pending invoices to generate new ones to request payment.
- Automate your process - Consider setting up a system or using software that can automatically generate and send invoices based on predetermined criteria, such as the completion of a project or the delivery of goods and services. This can help ensure a timely process.
💡 Tip: To avoid delayed payments or having to send follow-up memos, you can encourage your customers to pay on time by including an early payment discount and late payment fees on the invoice. You could also add a disclaimer that says you have the right to take legal action on overdue payments.
3. Use a Consistent Invoice Numbering System
Every invoice needs an invoice number, which is essential in tracking the transaction as it identifies each unique invoice. We recommend using a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters that reflect the date, project name, code, etc., to avoid duplication.
4. Offer Various Payment Methods
Offering various payment methods can increase your chance of getting paid faster since your customers can choose to pay in the most convenient way. It is essential to provide flexibility, especially for cross-border payments in multiple currencies.
Here are some payment methods that are applicable to both domestic and international payments:
- Bank transfer or wire transfer - This refers to a direct transfer from one bank account to another. It is a secure and reliable method to transfer a large amount of money, but it is not the fastest option.
- Online payment - This is the fastest way to make payment, and it is often done through online third-party providers such as PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Venmo.
- Credit cards and debit cards - This is another convenient and quick method for those who don't have access to a third-party payment provider. However, it may be subjected to high transaction fees.
5. Send a Reminder
Sending reminders before and after an invoice is due can save time and effort in the long run. You can send a reminder through email or set up an automatic notification with the invoice management software that you’re using.
If you're reminding the client about an upcoming payment, consider sending it one week before the due date. If the payment is overdue, you should notify the client promptly after the due date, one week after, and again after one month.
As a customer, it is also a good practice to set up a reminder after you've received and reviewed the invoice to ensure you make a payment on time.
💡 Tip: If you're sending a reminder through an email, keep your tone professional but also friendly. Mention the invoice number clearly in the subject line, and include all relevant information, such as the amount due and the due date, in the body of the email. You may also attach a copy of the invoice for convenience.
6. Set No More Than a One-Month Due Date
It is also crucial to set the right due date for invoice payments. While it mainly depends on the type of invoice you're using and your business's terms, an ideal payment due date should not extend beyond one month after the issue date.
Writing out the due date fully can also avoid confusion, as some countries use different date formats, such as DD-MM-YYYY or MM-DD-YYYY.
7. Keep a Digital Backup
Keeping invoices digitally can help prevent information loss. Cloud-based services, like Dropbox or OneDrive, are great options as they offer encryption and backup features that can provide more security than local devices.
Here are the most popular services that you can use to digitally backup your invoices.
- Dropbox - Store files, cloud content, paper docs, and web shortcuts in one place, with password protection, expiring links, and download permission features.
- OneDrive - Provides file sharing, editing, collaborating, and PC sync services. Compatible with Microsoft Office software like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint.
- Google Cloud Storage - A private and secure data storage by Google that can store, backup, archive, and deliver media and content. It has built-in data security that can be configured according to specific requirements.
- Apple iCloud - A cloud storage service available for Apple devices. It has features like a password management system (iCloud Keychain), synchronized multi-app editing and sharing, and backups.
8. Use a Tidy Invoice Layout
Not only does an invoice template with scattered and disorganized information confuse your clients, but it also creates an unprofessional impression for your business.
To ensure that your business always receives payments on time, review your invoice template carefully to be certain that the details, like the total amount, are correct and that the payment terms, including the due date, are written clearly and in a visible place.
A consistent and organized invoice template can enhance the efficiency of your business's invoicing management and overall operations. To achieve that, you can use invoice management software to design, customize, and manage invoices easily.
FAQs
What is the purpose of an invoice?
Generally, an invoice's purpose is to request payment and give both parties a clear transaction record. It is worth noting, however, that some types of invoices may serve other purposes besides collecting payment. For instance, commercial invoices can also be used for customs purposes.









